Pi Supercomputer
Following on from base Ubuntu build here I begin to look at Parrallel Programming.
Parrallel Programming
Each Raspberry Pi is a small unit of compute, one of my goals is to understand how operating many in a cluster. There are various approaches to parallel computational models, message-passing has proven to be an effective one. MPI the Message Passing Interface, is a standardized and portable message-passing system designed to function on a wide variety of parallel computers.
My prefered language is Python and usefully there is MPI for Python.
sudo apt-get install -y libopenmpi-dev python-dev pip
sudo pip install mpi4py
mpirun --version
All the RPIs in the cluster will access each other via SSH, this communication needs to be passwordless. The first thing you need to do is generate an SSH key pair on first host.
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
Once key generated to enable passwordless access, upload a copy of the public key to the other three servers.
ssh-copy-id ubuntu@[server_ip_address]
Repeat keygen and copy public key process on all four hosts.
In order for mpi to distribute workload the node where execution occurs needs to understand which nodes are available. The machinename parameter can be used to point to a text file containing list of nodes.
In order name we can use names we can add entries to hosts file.
sudo sh -c 'echo "192.168.1.100 rpi-0" >> /etc/hosts'
sudo sh -c 'echo "192.168.1.101 rpi-1" >> /etc/hosts'
sudo sh -c 'echo "192.168.1.102 rpi-2" >> /etc/hosts'
sudo sh -c 'echo "192.168.1.103 rpi-3" >> /etc/hosts'
We can then create a file in home directory listing nodes.
cat <<EOF >> ~/machinefile
rpi-0
rpi-1
rpi-2
rpi-3
EOF
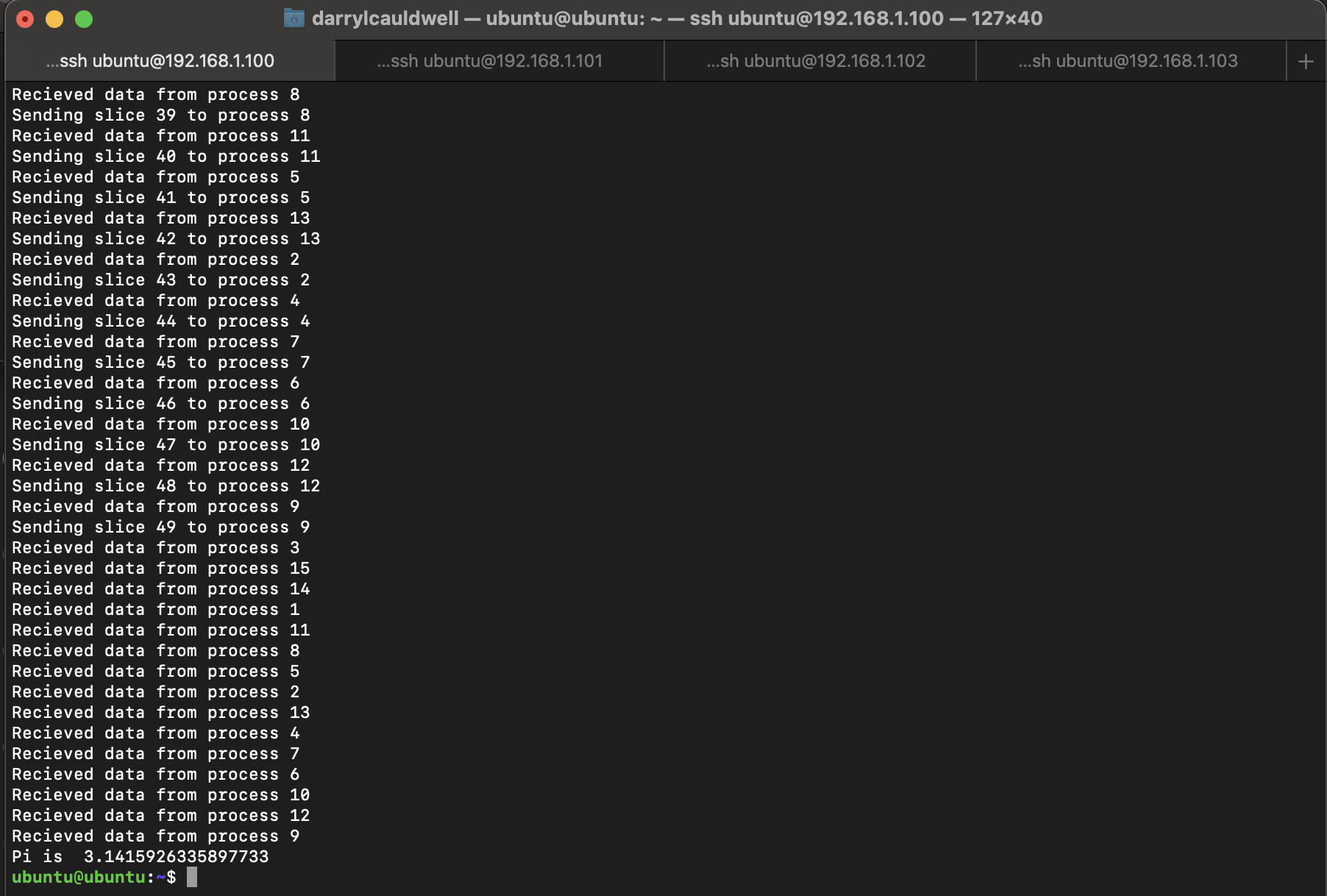
The easiest way to run commands or code is with the mpirun command. This command, run in a shell, will launch multiple copies of your code, and set up communications between them. As each Pi has four cores and we have four we can specify number of processors to run as sixteen.
mpirun -np 16 -machinefile ~/machinefile vcgencmd measure_temp
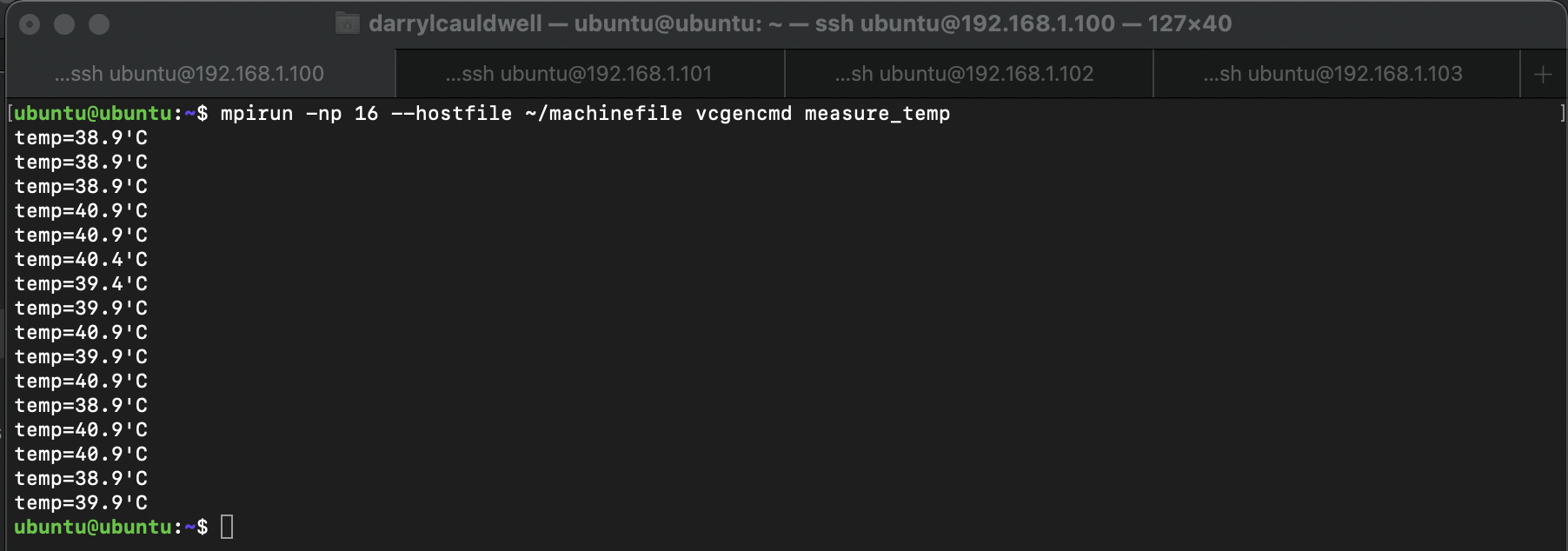
While its interesting running individual commands across nodes the MPI for Python module exposes options for programs to spread load. A simple test of this is where we scatter a bunch of elements, like those in a list, to processing nodes.
cat <<EOF >> ~/scatter.py
from mpi4py import MPI
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
size = comm.Get_size()
rank = comm.Get_rank()
if rank == 0:
data = [(x+1)**x for x in range(size)]
print ('we will be scattering:',data)
else:
data = None
data = comm.scatter(data, root=0)
print ('rank',rank,'has data:',data)
EOF
Once script created execute:
mpirun -np 16 -machinefile ~/machinefile python3 ~/scatter.py
While scattering elements of a list is interesting splitting up a processing problem and distributing to multiple processing nodes is more fun. Calculating Pi is a nice example of this, and its nice for a Pi cluster to calculate Pi with MPI.
#pi.py
from mpi4py import MPI
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
rank = comm.Get_rank()
size = comm.Get_size()
slice_size = 1000000
total_slices = 50
# This is the controller node.
if rank == 0:
pi = 0
slice = 0
process = 1
print (size)
# Send the first batch of processes to the nodes.
while process < size and slice < total_slices:
comm.send(slice, dest=process, tag=1)
print ("Sending slice",slice,"to process",process)
slice += 1
process += 1
# Wait for the data to come back
received_processes = 0
while received_processes < total_slices:
pi += comm.recv(source=MPI.ANY_SOURCE, tag=1)
process = comm.recv(source=MPI.ANY_SOURCE, tag=2)
print ("Recieved data from process", process)
received_processes += 1
if slice < total_slices:
comm.send(slice, dest=process, tag=1)
print ("Sending slice",slice,"to process",process)
slice += 1
# Send the shutdown signal
for process in range(1,size):
comm.send(-1, dest=process, tag=1)
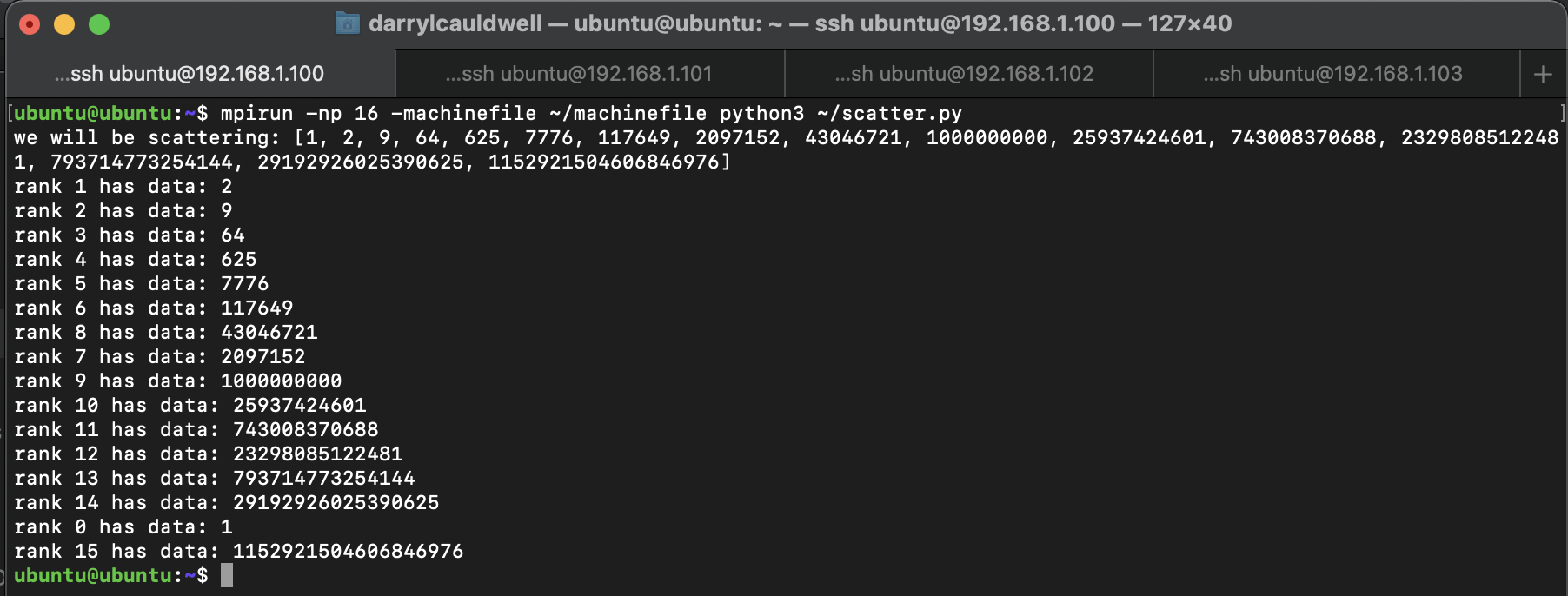
print ("Pi is", 4.0 * pi)
# These are the worker nodes, where rank > 0. They do the real work
else:
while True:
start = comm.recv(source=0, tag=1)
if start == -1: break
i = 0
slice_value = 0
while i < slice_size:
if i%2 == 0:
slice_value += 1.0 / (2*(start*slice_size+i)+1)
else:
slice_value -= 1.0 / (2*(start*slice_size+i)+1)
i += 1
comm.send(slice_value, dest=0, tag=1)
comm.send(rank, dest=0, tag=2)
Execute script with mpi and watch it distribute the calculation around the nodes and aggregate these to final answer.
mpirun -np 16 -machinefile ~/machinefile python3 pi.py