Introduction To Kubernetes Cluster Networking with Antrea

What is Antrea
Antrea is Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin for Kubernetes. The Antrea CNI leverages Open vSwitch (OVS) to provides an overlay network and security services for a Kubernetes cluster. The overlay encapsulation uses Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) by default, although Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation (GENEVE), Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) or Stateless Transport Tunneling (STT) encapsulation can be configured. Antrea is an open source project hosted on GitHub here. Using OVS also introduces other standard network management capabilities such NetFlow, sFlow, IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN).
Architecture
Antrea is composed of several components deployed as Pods in the kube-system namespace of the cluster. The Antrea Conroller monitors the addition and deletion of objects by watching the Kubernetes API. A daemonset is deployed which druns Antrea Agent on each node the Agent applys flow configuration to Open vSwitch (OVS).
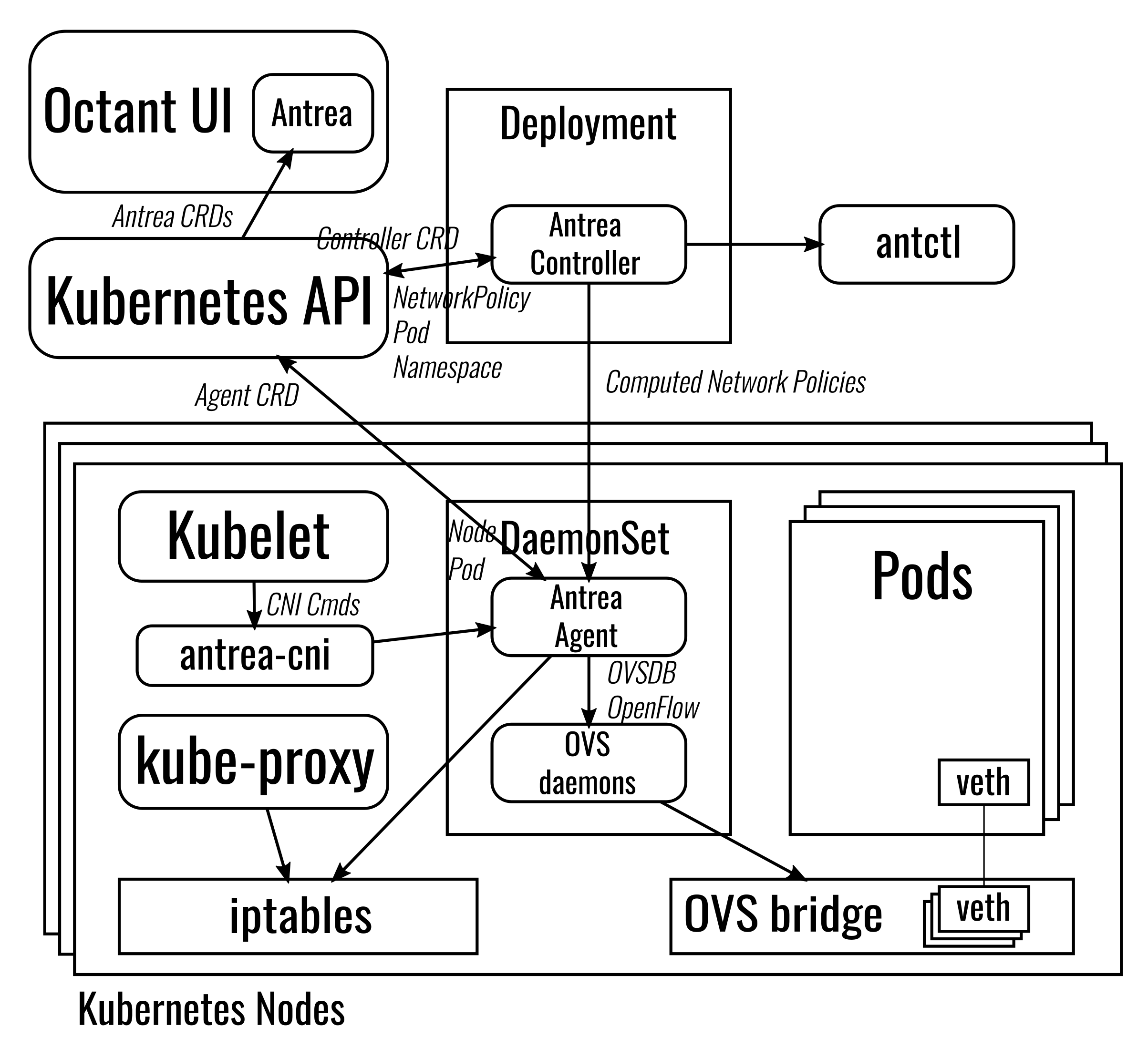
The network configration required by Kubernetes is configured in a collection of Open vSwitch (OVS) flow tables. To make it easy to interpret each type of network traffic is classified and each traffic classification is stored in its own flow table.
Creating A Simple Antrea Lab
We can create a lab to look at Antrea anywhere we can run some VMs so on either a public cloud or a homelab. Create three Ubuntu 19.10 VMs with 2x CPU, 4GB RAM and 50GB vHDD, use Netplan to configure NIC to static IP addressing like.
cat /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
ens160:
addresses:
- 192.168.1.27/24
gateway4: 192.168.1.254
nameservers:
search:
- darrylcauldwell.com
addresses:
- 192.168.1.10
Antrea requires Kubernetes 1.16 or later. Install Docker, Open vSwitch and Kubernetes by running the following.
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt install docker.io python apt-transport-https openvswitch-switch -y
sudo gpasswd -a $USER docker
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-add-repository "deb http://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main"
sudo apt-get update
sudo swapoff -a
sudo sed -i '/ swap / s/^\(.*\)$/#\1/g' /etc/fstab
sudo apt-get install -y kubelet=1.16.4-00 kubeadm=1.16.4-00 kubectl=1.16.4-00
To form the overlay network Antrea requires an IP address block to allocate IP addresses (–pod-network-cidr). We can use kubeadm to configure the IP address block and bootstrap the cluster by running the following:
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=172.16.0.0/16
In order to easily run kubectl from the master we can copy the kube config to our user profile by running the following.
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
With the control plane initiatlised we can now get the cluster token from the master we can use this to add the two worker Nodes to the cluster.
sudo kubeadm join 192.168.1.27:6443 --token 4bp2f0.ppfjk7mfee89j2kd \
> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:5e79610f28840c15be46895340c4a5535b9a0d003741ed657961891a05987ccd
All the Antrea components are containerized and can be installed using the Kubernetes deployment manifest. We can apply the default Antrea manifest supplied in GitHub repository which will deploy all necessary components.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vmware-tanzu/antrea/master/build/yamls/antrea.yml
The Antrea components are deployed to the kube-system Namespace. The components include Deploymentm, Pods, Daemonset and ConfigMap.
kubectl get all --namespace kube-system
kubectl get configmap --namespace kube-system
The ConfigMap defines antrea-agent.conf this is used by Daemonset on each Node to configure Open vSwitch for use with CNI we can see some key information like.
kubectl describe configmap antrea-config-tm7bht9mg6
Integration Bridge name (default: br-int)
DataPath type (default: system)
Interface name to communicate with host (default: gw0)
Tunnel (Encapsulation) type (default: vxlan)
MTU value (default: 1450)
Service CIDR (default 10.96.0.0/12)
Exploring The Open vSwitch Overlay Network
With Antrea in place we can look at exploring the overlay network it has put in place. We create a Kubernetes Namespace and deploy an simple stateless application like guestbook.
kubectl create -f https://k8s.io/examples/admin/namespace-dev.json
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=development
kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/guestbook/redis-master-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/guestbook/redis-master-service.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/guestbook/redis-slave-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/guestbook/redis-slave-service.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/guestbook/frontend-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/guestbook/frontend-service.yaml
When running we can view the Pods IP addressing.
kubectl get pods --output wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
frontend-6cb7f8bd65-25qv4 1/1 Running 0 5m47s 172.16.2.4 antrea-worker-2 <none> <none>
frontend-6cb7f8bd65-mn5jk 1/1 Running 0 5m47s 172.16.1.5 antrea-worker-1 <none> <none>
frontend-6cb7f8bd65-nr9zk 1/1 Running 0 5m47s 172.16.2.5 antrea-worker-2 <none> <none>
redis-master-7db7f6579f-4wdnj 1/1 Running 0 5m51s 172.16.2.2 antrea-worker-2 <none> <none>
redis-slave-7664787fbc-5xrvj 1/1 Running 0 5m49s 172.16.1.4 antrea-worker-1 <none> <none>
redis-slave-7664787fbc-nj6m5 1/1 Running 0 5m49s 172.16.2.3 antrea-worker-2 <none> <none>
We can see that IPs from 172.16.1.0/24 are issued to Pods running on Node antrea-worker-1 and 172.16.2.0/24 are issued to Pods running on Node antrea-worker-2. To facilitate communications between Pods the antrea-agent configures flows on Open vSwitch on each Node. If we connect to a Antrea Agent container we can see that an OVS bridge is created called br-int and the bridge has a vxlan tunnel port called tun0 and a gateway port called gw0. The internal port gw0 is allocated the role of gateway of the Node’s subnet and is allocated the first IP address in subnet.
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=kube-system
kubectl get pods --selector=component=antrea-agent --output wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
antrea-agent-czksb 2/2 Running 0 14m 192.168.1.28 antrea-worker-1 <none> <none>
antrea-agent-gwkmr 2/2 Running 0 14m 192.168.1.27 antrea-master <none> <none>
antrea-agent-x9xjk 2/2 Running 0 14m 192.168.1.29 antrea-worker-2 <none> <none>
kubectl exec -it antrea-agent-czksb -c antrea-ovs bash
ovs-vsctl list-br
ovs-vsctl show
3cf39eec-f64c-49ed-ad86-48f203b215a4
Bridge br-int
Port "tun0"
Interface "tun0"
type: vxlan
options: {key=flow, remote_ip=flow}
Port "coredns--886217"
Interface "coredns--886217"
Port "redis-sl-b32512"
Interface "redis-sl-b32512"
Port "coredns--3d5851"
Interface "coredns--3d5851"
Port "gw0"
Interface "gw0"
type: internal
Port "frontend-1ee3a9"
Interface "frontend-1ee3a9"
ovs_version: "2.11.1"
We can also see that ArpResponderTable (20) and L3ForwardingTable (70) have flow records relating to the pod network.
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=kube-system
kubectl exec -it antrea-agent-czksb -c antrea-ovs bash
ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-int | grep 172.16.2
cookie=0xf70e020000000000, duration=820.733s, table=20, n_packets=1, n_bytes=42, idle_age=585, priority=200,arp,arp_tpa=172.16.2.1,arp_op=1 actions=move:NXM_OF_ETH_SRC[]->NXM_OF_ETH_DST[],mod_dl_src:aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff,load:0x2->NXM_OF_ARP_OP[],move:NXM_NX_ARP_SHA[]->NXM_NX_ARP_THA[],load:0xaabbccddeeff->NXM_NX_ARP_SHA[],move:NXM_OF_ARP_SPA[]->NXM_OF_ARP_TPA[],load:0xac100201->NXM_OF_ARP_SPA[],IN_PORT
cookie=0xf70e020000000000, duration=820.733s, table=70, n_packets=649, n_bytes=63996, idle_age=0, priority=200,ip,nw_dst=172.16.2.0/24 actions=dec_ttl,mod_dl_src:06:d1:bb:d3:bc:fa,mod_dl_dst:aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff,load:0x1->NXM_NX_REG1[],load:0x1->NXM_NX_REG0[16],load:0xc0a8011d->NXM_NX_TUN_IPV4_DST[],resubmit(,105)
We can look to test the IP routing and connectivity between Pods on same Node and also between Nodes,
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=development
kubectl get pods --output wide | grep frontend
frontend-6cb7f8bd65-25qv4 1/1 Running 0 12m 172.16.2.4 antrea-worker-2 <none> <none>
frontend-6cb7f8bd65-mn5jk 1/1 Running 0 12m 172.16.1.5 antrea-worker-1 <none> <none>
frontend-6cb7f8bd65-nr9zk 1/1 Running 0 12m 172.16.2.5 antrea-worker-2 <none> <none>
kubectl exec -it frontend-6cb7f8bd65-25qv4 -- ping -c 1 172.16.2.5
kubectl exec -it frontend-6cb7f8bd65-25qv4 -- ping -c 1 172.16.1.5
Exploring Network Policy
Antrea implements NetworkPolicy using OVS Flows. Flows are organized in tables, and they are applied on each node by the Antrea agent. Before applying a network policy, we can check flow table IngressDefault (100) and IngressRuleTable (90)
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=kube-system
kubectl get pods | grep antrea-agent
kubectl exec -it antrea-agent-czksb -c antrea-agent ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-int | grep table=100
cookie=0xcac6000000000000, duration=9103.902s, table=100, n_packets=102, n_bytes=9696, priority=0 actions=resubmit(,105)
kubectl exec -it antrea-agent-czksb -c antrea-agent ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-int | grep table=90
cookie=0xcac6000000000000, duration=4059.159s, table=90, n_packets=32493, n_bytes=6556290, priority=210,ct_state=-new+est,ip actions=resubmit(,105)
cookie=0xcac6000000000000, duration=4059.159s, table=90, n_packets=1634, n_bytes=122104, priority=210,ip,nw_src=172.16.1.1 actions=resubmit(,105)
cookie=0xcac6000000000000, duration=4059.159s, table=90, n_packets=37, n_bytes=3768, priority=0 actions=resubmit(,100)
We can confirm that frontend can ping the backend.
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=development
kubectl get pods -o wide
kubectl exec -it frontend-6cb7f8bd65-25qv4 -- ping -c 1 172.16.2.27
We can create a network policy to deny all ingress.
cat <<EOF >/tmp/deny-all.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: default-deny
spec:
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress
EOF
kubectl create -f /tmp/deny-all.yaml
If we test again we can test and ensure that the policy is applied and the frontend can no longer ping backend.
kubectl exec -it frontend-6cb7f8bd65-25qv4 -- ping -c 1 172.16.2.27
We can then check IngressDefault (100) flow table and see that our network policy has added action to drop.
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=kube-system
kubectl exec -it antrea-agent-czksb -c antrea-agent ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-int | grep table=100
cookie=0xcac6000000000000, duration=3.427s, table=100, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=200,ip,reg1=0xa actions=drop
cookie=0xcac6000000000000, duration=3.427s, table=100, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=200,ip,reg1=0x8 actions=drop
cookie=0xcac6000000000000, duration=9226.746s, table=100, n_packets=137, n_bytes=12966, priority=0 actions=resubmit(,105)
